
Ethics and responsible AI in Generative Systems
AI’s transformative role demands ethical reflection: Ensuring fairness, reducing bias, protecting privacy, and preventing misuse.
Written by Marcus Hartmann, Felix Baumann, Maria Foelster and Joshua Wenn. Data is the fundamental building block in the field of artificial intelligence (AI), providing the potential for innovation and enabling Generative AI (GenAI) to showcase its capabilities. GenAI, a unique area within AI, learns from vast datasets to produce content, artwork, and writings, with data being the key to these creations often rivaling or exceeding human achievements. But why exactly is that?
Diverse and high quality data sets are a must for several reasons. For starters a wide array of data enables generative AI models to create a wider and more adaptable range of results. This is crucial for tasks such as generating text, synthesizing images, or composing music, where various individuals may possess distinct preferences and needs. By being trained on diverse data, the AI can effectively meet the demands of a broad audience and avoid producing biased results.
“In order for GenAI to operate with utmost efficiency and effectiveness, a vast assortment of diverse data is imperative.”
AI models that generate content can unintentionally create biased or offensive material if they are trained on a restricted and prejudiced dataset. The greater the inadequacy of data quality, the higher the probability and magnitude of bias. Employing varied and top-notch datasets aids in diminishing this bias by introducing the model to a wider array of viewpoints and encounters making them more robust.
To put it briefly, having a wide range of top-notch data sets is crucial when it comes to teaching reliable, flexible, morally upright, versatile AI models that can tackle an extensive array of tasks and inputs. It’s an important factor in ensuring the effectiveness and responsible use of AI in various applications.
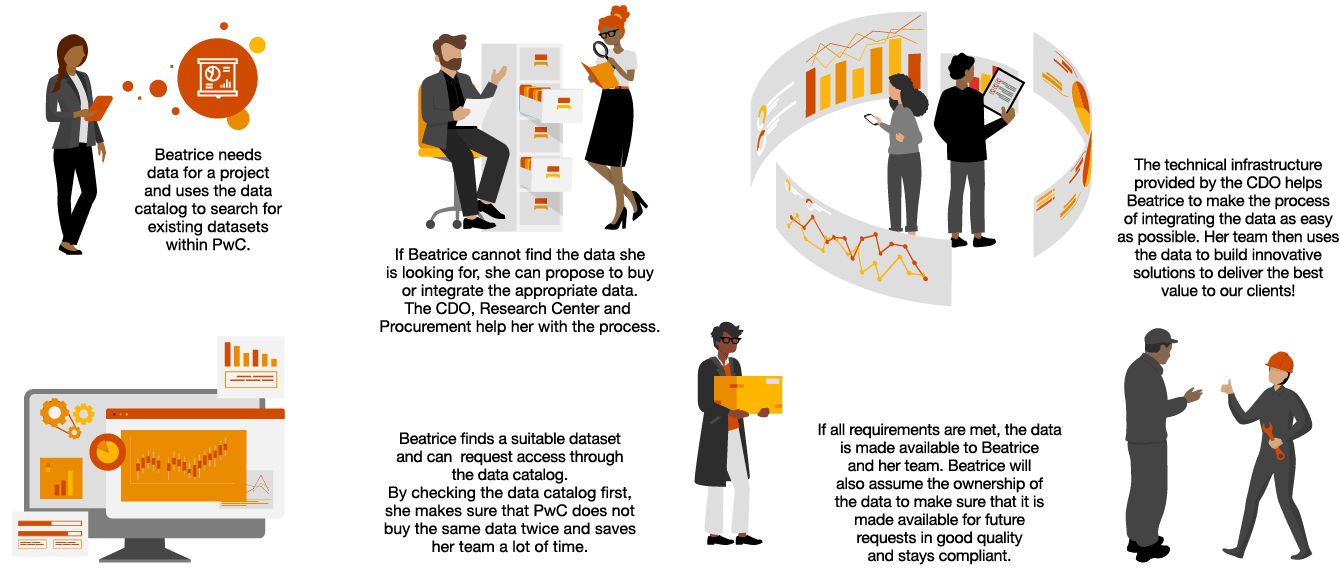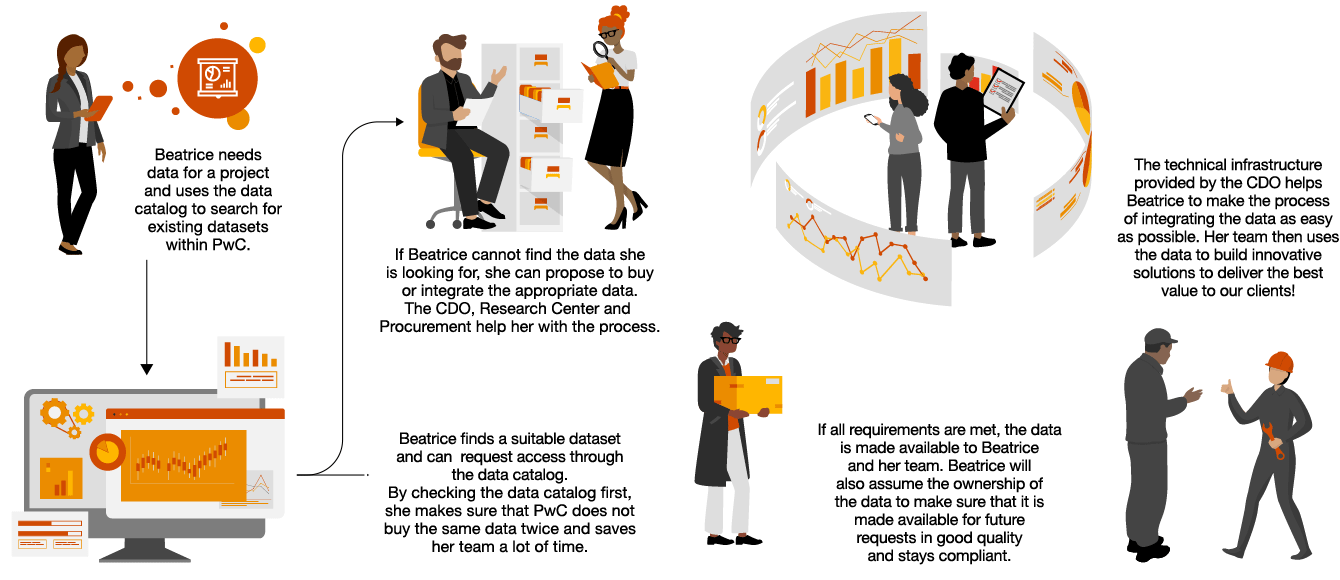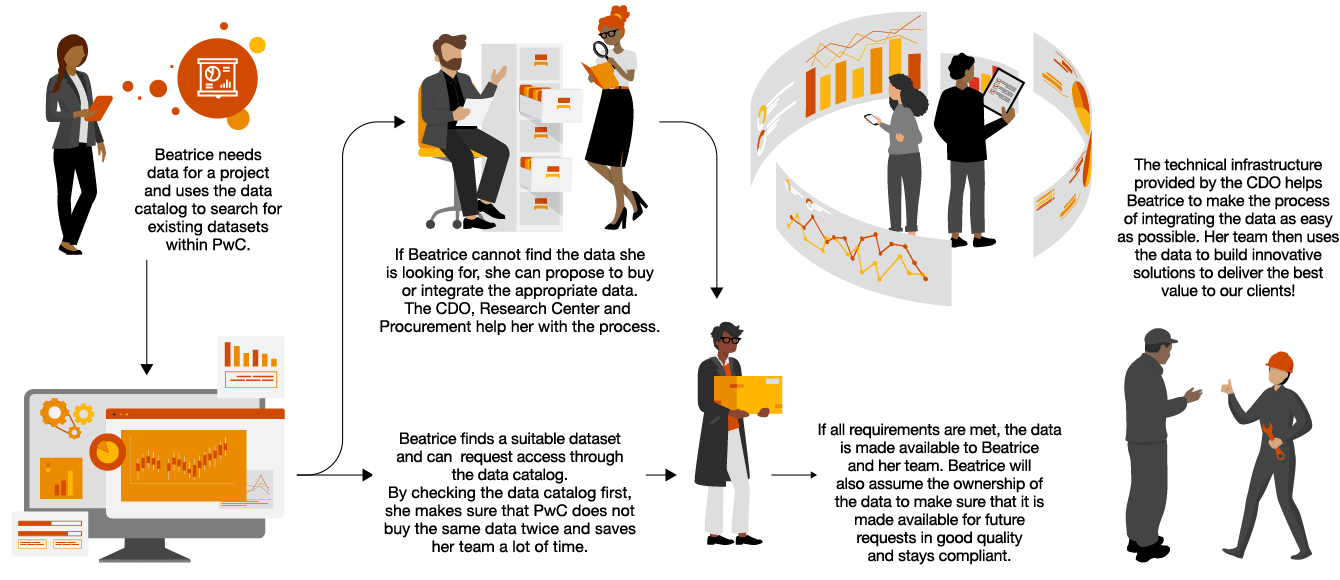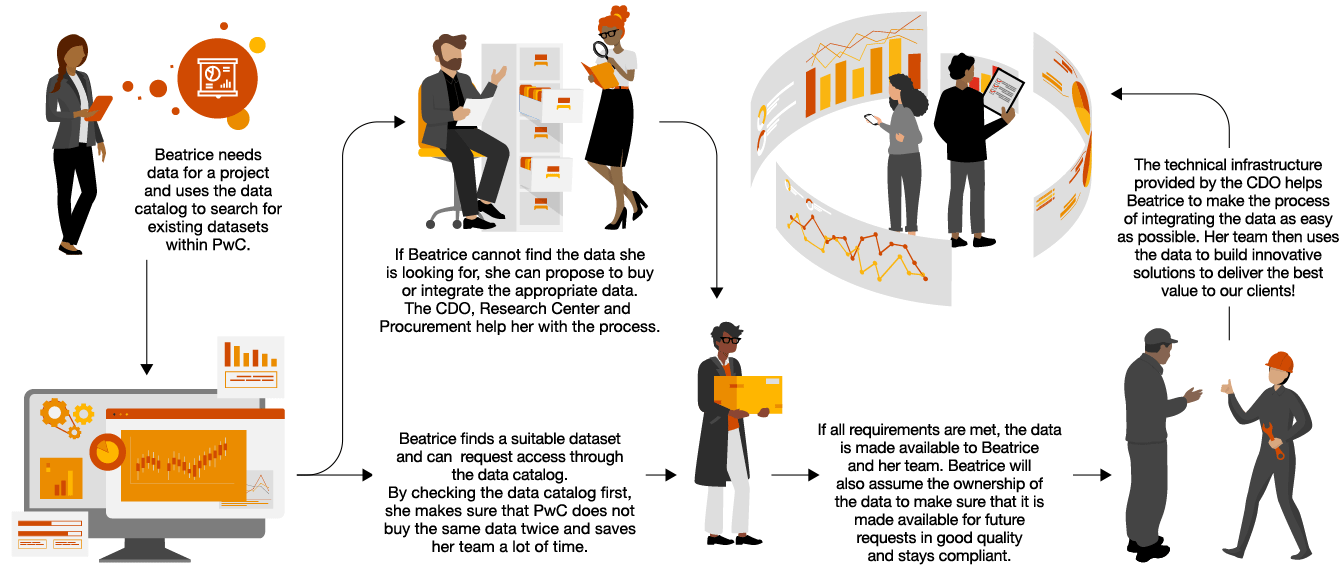
Now that we know why a diverse range of data sets is important next up is how to achieve such diversity. A proven method at PwC is the data acquisition process.
“Data acquisition describes a data type-dependent and standardized process for capturing and making data available for later analysis and use.”
It is important to note that data acquisition refers to data that has been purchased through a provider. It is in contrast to data integration, which refers to the process through which we make data that PwC already owns available. At PwC DE the Chief Data Office has the Service Ownership for Third Party Data Acquisition with following responsibilities and its advantages:
“Policies and use cases need to be defined to guide all industries on their GenAI journey – supported by a well established data governance framework.“
It becomes simpler to comprehend various subjects when they are explained through a systematic approach. To provide context: PwC follows the data lifecycle in its operations. Similar to any merchandise, data also undergoes a lifecycle.
Data cannot be captured at one single point. A holistic view of its entire lifecycle enables us to manage data so that it is fit for purpose at any given time. The data lifecycle covers the period starting from the first contact with the data when it is generated to the last point of contact, the final deletion. This general process describes the flow of data through an organization. Data passes through various points in the data lifecycle.
When collecting data GenAI can be used to augment collected data. This means it has the ability to add further samples or instances to expand the data set which leads to a more robust analysis. GenAI can also be helpful to add easier to consume documentation for data sources, based on specific metadata.
Risk: Adding GenAI to your data collection step enhances the risk of data biases, as it can perpetuate biases in your training data, and possible privacy concerns.
Do:
Don’t:
Data holds a significant position in the realm of Generative AI, serving as one of its fundamental components. Throughout the entire data lifecycle, there exist extensive possibilities for GenAI to contribute towards achieving enhanced efficiencies.
“Ensure comprehensive integration between corporate strategy and data strategy.”
It becomes imperative to establish a solid foundation in data management within the company and foster a culture that values data among both employees and management. This needs to be integrated into the company’s overarching goals, then translated into a data strategy and implemented throughout operational structures.
Management plays a critical role in developing guidelines that encompass these aspects while fostering an overall environment focused on data. Without proper data governance, guidelines, and fundamental data literacy, there is potential for Generative AI to present risks which need to be reduced as much as possible.
“Whenever you use data at PwC there are one or several steps from the Data Value Chain that can help you work more efficiently. While the ideation and product management remain with you, the CDO enables and coordinates the processes that drive the value creation. The CDO’s Data & Content Team provides the foundational structure for both the technical realization, and the governing and operational capabilities such as a data catalog, a data ecosystem. The Data & Tech team builds the infrastructure that underpins all operations. Lastly, various layers of compliance and risk complete the picture which the CDO can help you navigate.“
PwC has both in-house and external knowledge, as well as state-of-the-art resources concerning data that can be efficiently used to leverage the immense potential of GenAI. If you need any help or support regarding this issue, feel free to reach out to our team of proficient specialists who are always ready to assist you.


Christine Flath
Leitungsteam Familienunternehmen und Mittelstand und Ihre Ansprechpartnerin für Transformationsthemen, PwC Germany
Tel: +49 171 5666490



