Your expert for questions

Daniela Hanauer
Partner, Compliance, Integrity and Digital Ethics, PwC Germany
Tel.: +49 1511 1720054
Email
German companies must catch up with the top 10 trend digital ethics
According to a forecast by PwC, German gross domestic product will increase by more than 11 percent by 2030 as a result of AI applications. However, the rapid pace of digitalization and the associated changes are also raising concerns. There is a lack of recognized ethical rules aimed at strengthening society's confidence in the digital economy.
A broad social acceptance of new technologies and business models can only be achieved if companies design their digital transformation in a values-oriented manner. Digital ethics plays a central role as a vital part of integrity-driven management in order to create a sustainable basis for interaction with customers, employees and other stakeholders. The focus here is on values-oriented compliance and the willingness of companies to ensure that their own values are respected.
Digital ethics asks for the right action and the good life under the conditions of digitalization. It examines the social, ecological and economic compatibility of digital technologies in their development and application. Accordingly, digital-ethical risks – but also opportunities – arise for every company.
Our white paper provides an overview of opportunities and challenges for responsible companies in the digital world. In this way, we would like to contribute to the public discourse and encourage companies to proactively deal with digital ethics and to successfully anchor it strategically and operationally.
The survey results at a glance
1. The focus of Companies is on the technical implementation of digitalization
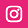
German companies also have to catch up in the general digitalization of their organization: only 33 percent rate the status of their transformation as positive (school grades ‘A’ or ‘B’). In contrast, the companies give a better rating for their focus on data protection and data security – 82 percent are extremely satisfied with this. However, this is not associated with a comprehensive concept of digital ethics. These results show that digitalization is still understood in Germany in a very technical way, while companies are lagging behind in developing new business models and mastering ethical challenges. However, how companies deal with ethical issues depends also on the industry – the pharmaceutical industry, for example, is comparatively advanced as a very strictly regulated industry.
How well positioned are companies in the field of digital ethics and digital responsibility?
2. The biggest challenge: Finding employees with the right skills
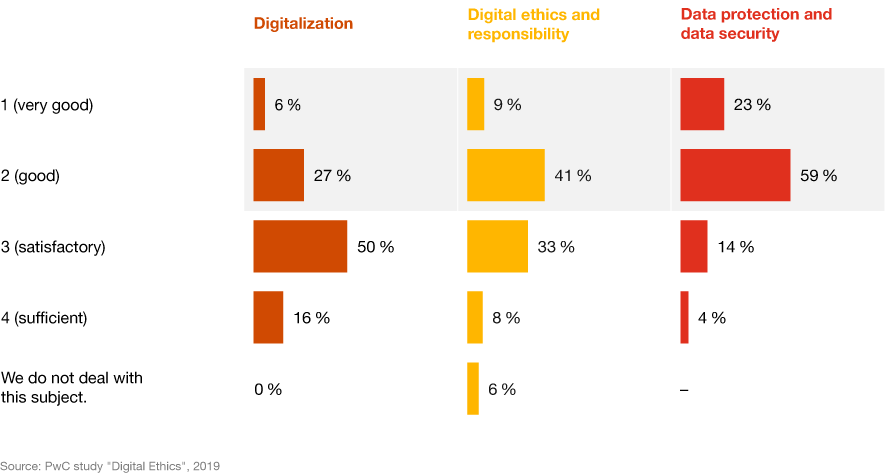
Why have so few companies so far been able to deal comprehensively with digital ethics and implement technologies accordingly? What factors impede companies in coping with ethical challenges? Above all, companies lack the right talents to develop and implement strategies, as 56 percent of decision-makers confirm. A further hurdle is the lack of awareness within the company of the importance of digital ethics – this stated 51 percent of survey participants. Other obstacles cited by the companies are the way employees handle digital information (44 percent) and unsuitable or outdated software solutions (35 percent). Scarce resources or unclear regulations in the area of artificial intelligence, on the other hand, play only a subordinate role.
What are the biggest challenges in implementing digital ethics strategies?
Corporate Digital Responsibility & Digital Ethics - Quick Check
Only 5 minutes to determine the degree of maturity of Digital Ethics in your company.
3. Digital ethics is one of the management tasks
Digital ethics already have a major influence on companies, as the study participants state – according to their assessment, particularly on the handling of sensitive information such as employee or customer data (85 percent), IT security systems (78 percent) and corporate culture in the digital world (62 percent). But ethical questions now also play a major role in creating transparency for employees, customers and stakeholders and in strategic decisions (59 percent each). Accordingly, digital ethics is highly valued within companies – 59 percent of the surveyed corporations deal with it at C-level. However, only one in five companies has a special representative for ethical challenges.
“Digital ethics is not a marginal topic for companies. Firms that establish rules and standards for a responsible approach to digitalization gain the acceptance of customers and the trust of society. This ensures their long-term business success.”
4. Only every fourth company works with formulated guidelines
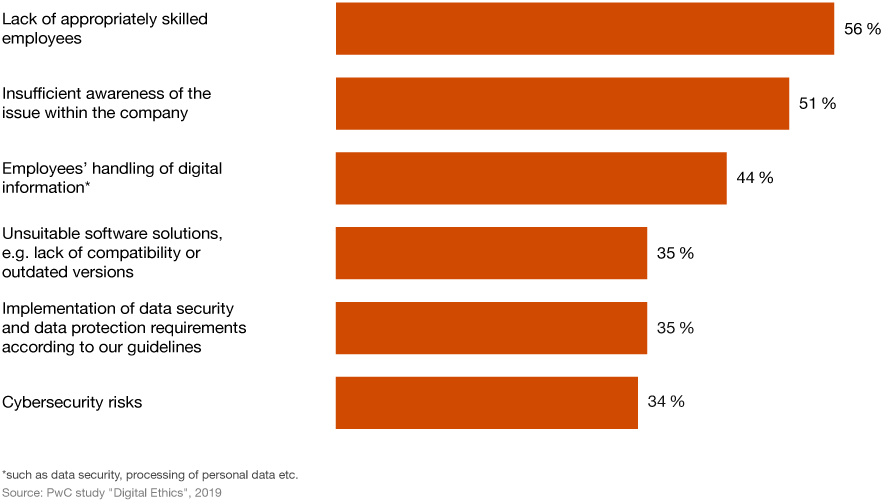
What measures are already being implemented by companies that associate them with digital responsibility? First and foremost are guidelines on data protection and the handling of personal data (78 percent) as well as guidelines for creating transparency regarding digital issues (57 percent). It is also important to the companies that decisions based on algorithms in the area of artificial intelligence can be corrected by humans (44 percent) and that there are binding guidelines for internal and external online communication (43 percent). Less widespread, on the other hand, are less developed standards on digital ethics and digital responsibility that could serve as guidelines for corporate decisions: Only a quarter of the companies use them to date. Just as few organizations have a fully formulated digital strategy with reference to digital ethics.
Which digital responsibility measures are being implemented?
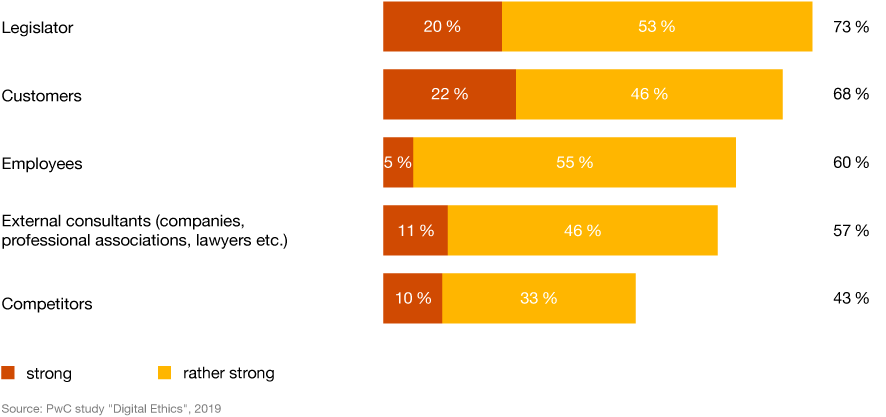
5. The legislator has the greatest influence on ethical issues
Companies are of great importance for economy and society – thus, many internal and external stakeholders influence the regulations on digital ethics in the organizations. The most important role is played by the legislator according to 73 percent of the survey participants, followed by customers and employees in second and third place (68 and 60 percent respectively). Other stakeholders such as competitors, investors or unions play a subordinate role.
Which stakeholders have an influence on internal company regulations on digital ethics?
“In the future, the topic of digital ethics will become even more important as the degree of digitalization increases. Companies will only be able to successfully manage the transformation if they win the trust of the people—through formulated ethical guidelines that ensure the responsible handling of people's personal data and privacy.”
Contact us